Bearings: Meaning, Examples, and Questions
Bearings are an essential concept in navigation. and geometry, commonly used to indibe directions and angles in real-world applications.
In this lesson you will learn what bearings are. You will also learn how to draw, measure, and calculate bearings (with lots of examples to practice).
What is a Bearing?
A bearing is an angle measured clockwise from the north direction.
Bearings are expressed with three digits, so they range from 000° (due north) to 360° (back to north).
For example, a bearing of 045° points northeast, 090° points east, and 180° points south. This system makes it easy to communicate directions accurately.
How to Draw a Bearing
- Identify the North direction: Start from a line pointing north, as bearings are measured clockwise from this point.
- Measure clockwise: Measure the angle clockwise from the north line to the desired direction.
- Express the angle in three digits: Ensure the bearing is written as a three-figure number (e.g., 035° instead of 35°).
Examples of Drawing Bearings
Example 1:
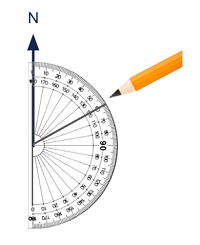
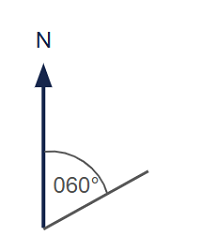
Draw a bearing of 060°
Method:
- Draw a line pointing North.
- Measure 60° clockwise from North.
- Label the angle using three digits.
Calculating Bearings
In order to calculate bearings you need to know basic angle facts including angles around a point, angles on a straight line, and angles in parallel lines.
Some question also require knowledge of trigonometry.
How to Calculate Bearings
- Identify the point that the bearing begins from.
- From this point, face north and turn clockwise until you are facing the second point.
- Use angle facts to calculate this missing angle.
- Write the answer as a 3 digit bearing.
You have now identified the angle to be calculated.
If the size of the angle is less than 100, write 0 before the number.
Examples of Calculating Bearings
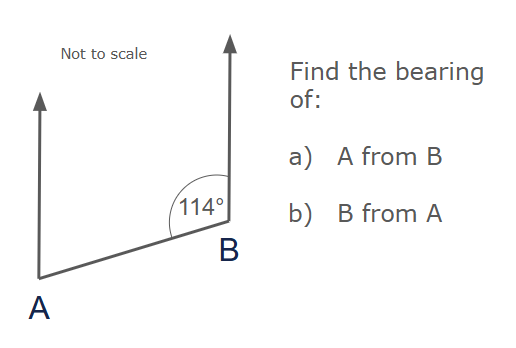
Example 1:
Calculate:
a) The bearing of B from A
b) The bearing of A from B
Exam Practice Questions
Ready to practise some past paper questions? Choose your syllabus: